GDPR Compliance Checklist: 8 Essential Steps for 2026
Johannes
Co-Founder
5 Minutes
February 3rd, 2026
Navigating the Labyrinth of GDPR: A Practical Checklist for Modern Teams
In an environment where data is a core asset, ensuring its protection is not just a legal obligation but a cornerstone of customer trust. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets the global standard for data privacy, but navigating its complexities can feel daunting. For modern teams using privacy-centric tools like Formbricks to gather user insights, aligning data handling practices with GDPR is crucial for responsible innovation. This comprehensive GDPR compliance checklist breaks down the regulation into eight manageable, actionable steps designed for practical implementation.
We will move beyond abstract principles to provide concrete examples, specific guidance, and clear implementation details. This article covers everything from conducting a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) and establishing a lawful basis for processing to managing data subject rights and responding to breaches. Each section is crafted to be a clear, step-by-step guide, offering actionable advice rather than vague theory. Whether you're a product manager refining user experiences, a marketer personalizing campaigns, or an engineer building new features, this guide equips you with the tools to build a robust, provable compliance framework.
Following these steps will help your organization not only avoid significant fines but also foster a culture of deep-seated respect for user privacy. While our checklist is comprehensive, certain activities like B2B marketing have their own nuances. For a deeper understanding and additional resources on that specific area, you can refer to a dedicated GDPR compliance checklist for B2B outreach. Now, let's dive into the essential components of a successful GDPR strategy.
1. Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA)
A Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) is a fundamental risk management process mandated by the GDPR. It’s a systematic evaluation designed to identify, assess, and mitigate the risks associated with data processing activities that are likely to pose a high risk to individuals' rights and freedoms. Think of it as a mandatory "look before you leap" for any new project, system, or technology involving personal data. Completing a DPIA isn't just a box-ticking exercise; it’s a critical step in building privacy-by-design into your operations and is a cornerstone of any robust GDPR compliance checklist.
You must conduct a DPIA before initiating any high-risk processing. This includes activities like large-scale processing of sensitive data (e.g., health or biometric information), systematic monitoring of public areas, or using new technologies like AI-driven profiling. For instance, a healthcare provider launching an AI diagnostic tool that analyzes patient data would require a DPIA. Similarly, a financial institution implementing a new biometric authentication system for its mobile app must first assess the potential impact on user privacy.
How to Conduct a DPIA
The process involves a methodical review of your intended data processing. You'll need to describe the nature, scope, context, and purpose of the processing. This includes mapping out what data you're collecting through tools like Formbricks, why you need it, and how you'll use it.
The following infographic illustrates the core workflow of a DPIA, breaking it down into three essential stages.
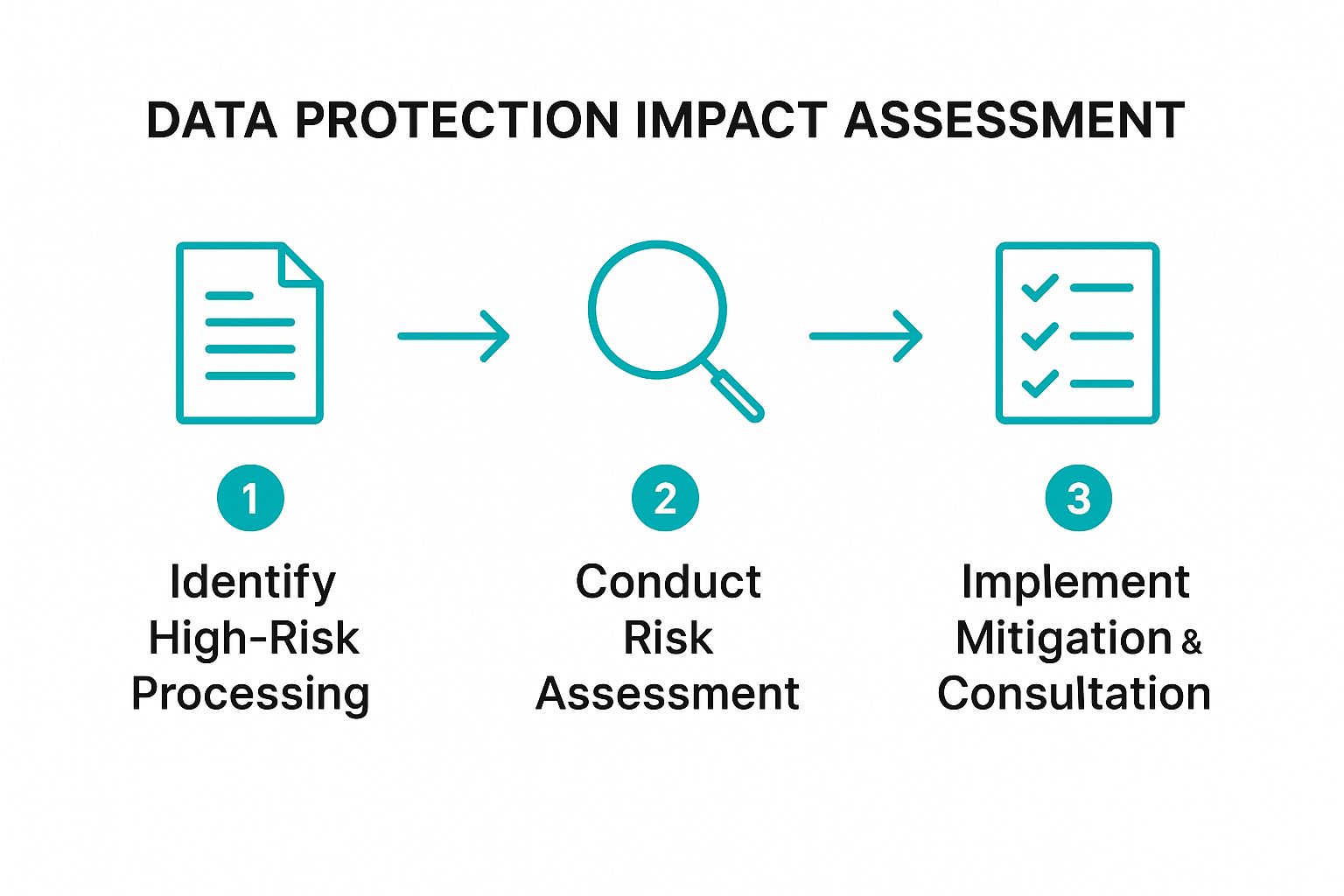
This process flow highlights that a DPIA is a proactive, sequential journey from identification to resolution, ensuring that risks are not just found but actively managed. If significant risks remain after implementing mitigation measures, you are legally required to consult with your supervisory authority before starting the processing.
Actionable Tips for an Effective DPIA:
- Involve Stakeholders Early: Don't conduct a DPIA in a silo. Involve your Data Protection Officer (DPO), IT security, legal teams, and relevant business units from the project's inception.
- Document Everything: Meticulously record every step of your assessment, from the risks identified to the mitigation measures you decide to implement. This documentation is your proof of compliance.
- Use Established Frameworks: Start with a recognized template, such as the one provided by the UK's Information Commissioner's Office (ICO) or your relevant national authority.
- Review and Update: A DPIA is a living document. It must be reviewed regularly and updated whenever there is a significant change to the nature, scope, or context of the processing.
2. Lawful Basis for Processing Personal Data
Identifying and documenting a lawful basis for processing is the legal bedrock of all your data-handling activities under the GDPR. You cannot process a single piece of personal data without first establishing a valid reason under Article 6. This choice isn't arbitrary; it dictates your obligations, including data subject rights and how long you can retain information. Failing to establish a lawful basis renders your processing unlawful from the start, making this a non-negotiable step in any GDPR compliance checklist.
You must determine your lawful basis before you collect and process any personal data. For instance, an e-commerce platform processing a customer's address to ship a product does so under the 'performance of a contract' basis. In contrast, when you collect email addresses for a marketing newsletter using a Formbricks form, you will almost certainly rely on 'consent'. Your HR department processes employee bank details for payroll based on a 'legal obligation'. Each distinct processing activity requires its own carefully considered lawful basis.
How to Determine and Document Your Lawful Basis
The process involves analyzing each data processing activity and aligning it with one of the six lawful bases defined in the GDPR: consent, contract, legal obligation, vital interests, public task, and legitimate interests. Your reasoning must be documented to demonstrate accountability. This means clearly recording why you chose a specific basis for a particular activity.
For example, if you're a SaaS company using customer data for product analytics, you might rely on 'legitimate interests'. This requires you to conduct a Legitimate Interests Assessment (LIA) to balance your business interests against the individual's rights and freedoms. This assessment must be documented as evidence of your due diligence.
Actionable Tips for Managing Lawful Bases:
- Document Your Decisions: Create and maintain a record of processing activities (ROPA) that explicitly states the lawful basis for each type of data processing, along with your justification for choosing it.
- Conduct Thorough Legitimate Interests Assessments (LIAs): If relying on legitimate interests, perform and document a three-part test: identify the legitimate interest, show the processing is necessary to achieve it, and conduct a balancing test against the individual's rights.
- Implement Robust Consent Management: When using consent, ensure it is freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous. Use tools to manage and record consent effectively, making it easy for users to withdraw it at any time.
- Train Your Team: Ensure all staff involved in data processing, from marketing to development, understand the different lawful bases and their specific requirements. This prevents misapplication and ensures compliance across the board.
- Review and Update Regularly: Your processing activities may change over time. Regularly review your stated purposes and lawful bases to ensure they remain accurate and appropriate. If your purpose for processing changes, you may need to identify a new lawful basis and inform the individuals.
3. Data Subject Rights Implementation
Empowering individuals with control over their personal data is a central tenet of the GDPR. This is achieved through a set of eight fundamental data subject rights, which your organization must be prepared to facilitate. Implementing robust procedures to handle these requests is not optional; it is a legal requirement and a critical component of any GDPR compliance checklist. These rights include access, rectification, erasure (the "right to be forgotten"), restriction of processing, data portability, and the right to object.
Your organization must establish clear, accessible, and efficient systems to respond to Data Subject Access Requests (DSARs) promptly. The standard timeframe for a response is one month, though this can be extended by two additional months for complex cases. Failing to meet these deadlines or adequately fulfill requests can result in significant fines and reputational damage. For instance, a user has the right to ask Spotify for a complete copy of their listening history via its data download feature, exercising their right to data portability. Similarly, a customer can use IKEA's online form to request the deletion of their account information, invoking their right to erasure.

This framework ensures that individuals remain the ultimate owners of their data, with the power to verify, correct, and remove it as they see fit. Handling these requests effectively demonstrates your organization's commitment to transparency and accountability.
How to Fulfill Data Subject Requests
The key is to create a standardized internal workflow that is triggered whenever a request is received, regardless of the channel. Your process should cover everything from initial identity verification to locating the relevant data across all systems, performing the requested action, and communicating the outcome back to the individual. You'll need to know exactly what data you hold, which is why accurate data mapping is a prerequisite. Capturing consent and preferences effectively through tools like Formbricks can also simplify this process, as you have a clear record from the outset. For a deeper look at how to structure these interactions, you can explore our comprehensive guide to GDPR surveys.
Actionable Tips for Effective Implementation:
- Standardize Your Intake Process: Create a dedicated and easily accessible channel for users to submit requests, such as a specific email address or an online portal like Microsoft's privacy dashboard.
- Develop Clear Internal Procedures: Document step-by-step instructions for your team on how to handle each type of right. This should include identity verification protocols to prevent data breaches.
- Train Your Team: Ensure that all staff, especially customer-facing teams, are trained to recognize and correctly route a data subject request.
- Maintain a Detailed Log: Keep a secure and confidential record of every request received, including the date, the nature of the request, the steps taken, and the date of your response. This log is crucial for demonstrating compliance.
- Automate Where Possible: For common requests like data access or deletion, consider implementing automated systems to reduce manual effort and minimize the risk of human error.
4. Privacy by Design and by Default
Privacy by Design and by Default is a proactive, preventative approach mandated by Article 25 of the GDPR. It requires organizations to embed data protection principles into the very fabric of their technologies, systems, and business practices from the outset, rather than treating privacy as an afterthought. "By design" means integrating privacy into every stage of development, while "by default" ensures that the most privacy-friendly settings are the standard, requiring no action from the user. This makes privacy a core component of system functionality and a key part of any effective GDPR compliance checklist.
This principle must be applied whenever you design a new product, service, or business process that involves personal data. For example, when building a new feature in your SaaS application, you should be considering data minimization and purpose limitation from the initial wireframes. A practical case is a social media platform that, by default, sets new user profiles to private instead of public. Similarly, a tool like Slack offers data residency controls, allowing organizations to choose where their data is stored, baking privacy considerations directly into its architecture.
How to Implement Privacy by Design and by Default
Adhering to this principle means shifting from a reactive compliance model to a proactive one. It involves a deep, foundational understanding of data privacy principles and integrating them into your project lifecycle. For teams using tools to gather user feedback, this means configuring your forms to collect only the essential data needed for that specific purpose.
At Formbricks, we champion this approach, ensuring our own systems and the tools we provide are built with privacy at their core. By making data protection a foundational element, we help our users meet their own compliance obligations effortlessly. You can explore how we integrate these concepts in our own platform and learn more about our commitment to privacy on formbricks.com.
Actionable Tips for Effective Implementation:
- Conduct Privacy Reviews Early and Often: Integrate privacy checkpoints into each stage of your development lifecycle, from concept and design to deployment and maintenance.
- Embrace Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs): Use technologies like pseudonymization, anonymization, and end-to-end encryption wherever possible to reduce the risk to personal data.
- Implement Data Minimization by Default: Design systems and forms to collect only the absolute minimum data required for a specific, legitimate purpose. Avoid "just-in-case" data collection.
- Provide Granular User Controls: Give users clear and easy-to-use controls over their data, ensuring default settings are always the most protective of their privacy.
- Train Your Development Teams: Regularly educate your engineers, product managers, and designers on data protection principles so they can make privacy-conscious decisions in their daily work.
5. International Data Transfer Compliance
The GDPR imposes strict regulations on the transfer of personal data outside the European Economic Area (EEA) to ensure that the level of protection afforded to individuals is not undermined. International data transfer compliance involves putting in place legally recognized mechanisms to safeguard this data when it crosses borders. This isn't merely a formality; it's a critical component of any GDPR compliance checklist, ensuring that data, no matter where it's processed, receives EEA-equivalent protection.
You must address international data transfers whenever your processing activities involve sending personal data to a third country or international organization. This applies if you use cloud services with servers located outside the EEA, have a global workforce, or partner with international vendors for data processing. For example, a European e-commerce company using a US-based marketing automation platform or a SaaS provider like Formbricks leveraging a non-EEA cloud infrastructure must implement a valid transfer mechanism. Similarly, large tech companies like Microsoft have responded by creating solutions such as the EU Data Boundary to keep customer data within the EU, underscoring the importance of this rule.
How to Ensure Compliant Data Transfers
The process requires identifying a lawful basis for the transfer under Chapter V of the GDPR. This often involves using "appropriate safeguards," with Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) being the most common. SCCs are model data protection clauses adopted by the European Commission that the data exporter and importer sign, contractually binding them to protect the data.
Following the Schrems II court ruling, simply signing SCCs is not enough. You must also conduct a Transfer Impact Assessment (TIA) to verify that the laws in the recipient country do not prevent the data importer from upholding their contractual obligations. If risks are identified, you must implement supplementary measures to mitigate them.
Actionable Tips for Secure International Transfers:
- Map All International Data Flows: Create a comprehensive record of all data transfers outside the EEA. Identify the data categories, the purpose of the transfer, the recipient country, and the data importer.
- Implement SCCs with Supplementary Measures: Adopt the latest version of the SCCs for all relevant transfers and conduct a thorough TIA for each. Document any supplementary measures taken, such as enhanced encryption or organizational policies.
- Regularly Review Transfer Mechanisms: The landscape of international data transfers is dynamic. Continuously monitor adequacy decisions (countries deemed safe by the EU Commission) and legal developments in third countries that could impact your transfers.
- Consider Data Localization: Where feasible, explore options to store and process EEA personal data exclusively within the EEA. This can simplify compliance by eliminating the need for a transfer mechanism.
- Maintain Detailed TIA Documentation: Keep meticulous records of your TIAs, including your assessment of third-country laws and the rationale for the supplementary measures you implemented. This documentation is your evidence of due diligence.
6. Data Breach Notification and Response
A robust Data Breach Notification and Response plan is a non-negotiable component of any GDPR compliance checklist. Under Article 33, organizations are mandated to detect, investigate, and report personal data breaches to the relevant supervisory authority. This notification must occur without undue delay and, where feasible, within 72 hours of becoming aware of the breach, especially if it's likely to result in a risk to individuals' rights and freedoms. This isn't merely a reactive measure; it's a critical process that demonstrates accountability and helps mitigate harm to affected individuals.

You must activate your response plan the moment a breach is suspected. If the breach poses a high risk to individuals, such as potential identity theft or financial loss, you must also communicate the breach directly to the affected data subjects without undue delay. For example, Marriott’s 2018 disclosure of the massive Starwood database compromise involved notifying both regulators and millions of affected customers due to the high-risk nature of the exposed data, including passport numbers and payment card information. This highlights the dual notification obligation that is central to GDPR compliance.
How to Manage Breach Response
Effective breach management requires a pre-established, well-rehearsed incident response plan. This plan should detail the immediate steps to contain the breach, assess the risk, and fulfill your legal notification duties. This includes identifying what data was compromised, how many individuals were affected, and the potential consequences.
For instance, if you discover that a vulnerability in your Formbricks survey setup has exposed user email addresses and sensitive responses, your plan should guide you through containing the leak, evaluating whether the exposure constitutes a high risk, and preparing the necessary notifications for both your supervisory authority and the affected users within the tight GDPR timeframes.
Actionable Tips for an Effective Breach Response:
- Develop and Test Your Plan: Don't wait for a breach to happen. Create a detailed incident response plan and conduct regular drills or tabletop exercises to ensure your team knows exactly what to do.
- Maintain Key Contact Lists: Keep an updated list of contacts for your supervisory authority, legal counsel, cyber insurance provider, and other key stakeholders to ensure you can communicate swiftly.
- Use Notification Templates: Prepare pre-approved breach notification templates for both authorities and data subjects. This ensures clarity, consistency, and speed when a real incident occurs.
- Document Everything Meticulously: Maintain a detailed breach log. Record the facts of the breach, its effects, and the remedial actions taken. This documentation is crucial for demonstrating accountability to regulators.
- Consider Cyber Insurance: Explore obtaining a cyber insurance policy. It can provide critical financial and logistical support during a breach, covering costs related to forensic investigation, legal fees, and customer notifications.
7. Records of Processing Activities (ROPA)
A Record of Processing Activities (ROPA) is a detailed, internal inventory of an organization's data processing operations. Mandated under Article 30 of the GDPR, it serves as a crucial accountability tool, providing a comprehensive overview of how personal data is handled. Think of it as a mandatory, detailed map of your data landscape, demonstrating to regulators and stakeholders that you understand and control your data flows. Maintaining a ROPA is a non-negotiable part of any serious GDPR compliance checklist, particularly for organizations with over 250 employees or those engaged in high-risk processing.
This requirement applies not only to large corporations but also to smaller businesses whose processing activities are frequent and could pose a risk to individuals' rights, or involve special categories of data. For example, a fintech startup processing financial transaction data, regardless of its size, must maintain a ROPA. Similarly, a global company like Siemens utilizes an automated ROPA management platform to maintain a dynamic and accurate inventory across its vast operations, ensuring ongoing compliance and operational transparency.
How to Create and Maintain a ROPA
Creating a ROPA involves a systematic documentation process for each distinct processing activity. You must capture specific details, including the purpose of processing, the categories of data subjects and personal data, any data recipients (including those in third countries), data retention schedules, and a description of the technical and organizational security measures in place. This includes data collected via tools like Formbricks for user feedback or lead generation.
The process requires a thorough audit of all departments to identify where and why personal data is being processed. This isn't a one-time task; the ROPA must be a living document, updated whenever new processing activities are introduced or existing ones are modified. For instance, Deutsche Bank maintains meticulously detailed processing records that are integrated into their risk management framework, allowing for continuous oversight and control.
Actionable Tips for an Effective ROPA:
- Use Standardized Templates: Create and enforce the use of a single, standardized template across the organization. This ensures consistency and makes the ROPA easier to review, audit, and update.
- Assign Clear Ownership: Designate a specific owner for each processing activity listed in your ROPA, typically the head of the relevant business unit. This accountability ensures that the record is kept current.
- Integrate ROPA into Workflows: Embed ROPA updates into your standard project management and change control processes. Before launching a new product or feature, make updating the ROPA a mandatory step.
- Implement Regular Review Cycles: Schedule periodic reviews (e.g., quarterly or semi-annually) of the entire ROPA with activity owners to confirm accuracy and make necessary adjustments.
8. Data Protection Officer (DPO) Appointment and Management
A Data Protection Officer (DPO) is an enterprise security leadership role mandated by the GDPR for certain organizations. This individual is an independent expert responsible for monitoring internal compliance, advising on data protection obligations, and acting as the primary contact point for data subjects and supervisory authorities. Appointing a DPO isn't just a regulatory formality; it’s a strategic move that embeds data protection expertise directly into your organizational fabric, making it a critical component of any GDPR compliance checklist.
The requirement to appoint a DPO is not universal. It becomes mandatory if your core activities involve large-scale, regular, and systematic monitoring of individuals (e.g., a social media platform analyzing user behavior) or large-scale processing of sensitive data categories or data relating to criminal convictions. For example, a hospital processing patient health records must have a DPO. Likewise, a tech company using behavioral advertising at scale would need one. Organizations can also appoint a DPO voluntarily as a matter of good practice.
How to Appoint and Manage a DPO
The DPO must have expert knowledge of data protection law and practices and must report directly to the highest level of management. This ensures their independence and authority. Their role is to inform, advise, and monitor, not to be personally responsible for compliance, which remains with the organization (the controller or processor). They can be an internal employee or an external consultant, as long as there is no conflict of interest with other duties. This process involves more than just a job title; it requires providing the DPO with the necessary resources and autonomy to perform their tasks effectively. To understand how a DPO's responsibilities align with vendor relationships, it's useful to review a Data Processing Addendum (DPA), which outlines the roles of controllers and processors.
The effectiveness of a DPO hinges on their integration within the company and the support they receive. For instance, Deutsche Telekom has established a comprehensive DPO program with a network of privacy professionals, ensuring consistent application of data protection principles across the entire group.
Actionable Tips for an Effective DPO:
- Clearly Define the DPO Role: Create a detailed job description that outlines the DPO's tasks, responsibilities, and position within the organization, ensuring it aligns with GDPR Article 39.
- Ensure Direct Access to Senior Management: The DPO must have a direct line to the board or C-suite to report on compliance and raise critical issues without delay.
- Provide Ongoing Training and Resources: Data protection is an evolving field. Support your DPO with continuous professional development, certifications (like those from the IAPP), and the budget for necessary tools.
- Prevent Conflicts of Interest: The DPO cannot hold a position that leads them to determine the purposes and means of processing personal data, such as Head of IT or Marketing Director.
- Regularly Review Effectiveness: Periodically assess whether the DPO has sufficient resources and authority to fulfill their duties and adjust as needed.
GDPR Compliance Checklist Comparison
| Item | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) | High – specialized expertise, time-consuming | High – requires expertise, stakeholder input | Identifies privacy risks, reduces breaches | High-risk data processing projects (e.g., surveillance, biometrics) | Proactive risk mitigation, regulatory compliance |
| Lawful Basis for Processing Personal Data | Moderate – legal assessment before processing | Moderate – legal and compliance resources | Legal foundation for processing activities | All personal data processing activities | Clear legal basis, supports accountability |
| Data Subject Rights Implementation | High – complex technical and procedural setup | High – systems, training, verification systems | Enhanced transparency and user trust | Organizations handling frequent data subject requests | Builds trust, competitive advantage |
| Privacy by Design and by Default | Moderate to High – requires privacy expertise | Moderate – design phase involvement | Reduced privacy risks from system design | Product and system development requiring data protection by default | Cost-effective risk reduction, innovation |
| International Data Transfer Compliance | High – complex legal, contractual, and monitoring | High – legal, compliance, and technical controls | Ensures lawful cross-border data flows | Organizations transferring personal data outside EEA | Flexibility in mechanisms, international compliance |
| Data Breach Notification and Response | High – tight deadlines, complex incident handling | High – investigation teams, documentation | Rapid risk mitigation, regulatory compliance | Any organization handling personal data | Quick response, reduces penalties |
| Records of Processing Activities (ROPA) | Moderate – ongoing record keeping and coordination | Moderate to High – depends on org size | Demonstrates accountability and compliance | Large organizations, high-risk processing | Comprehensive data overview, supports audits |
| Data Protection Officer (DPO) Appointment | Moderate to High – requires expert appointment | Moderate to High – salary/training, independence | Central compliance expert, single contact point | Public authorities, large-scale monitoring, special category processing | Expertise, improves compliance culture |
From Checklist to Culture: Embedding Privacy into Your DNA
Navigating the intricacies of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) can feel like a monumental task. By working through this comprehensive GDPR compliance checklist, you've taken a critical first step, moving from uncertainty to a structured, actionable plan. You now possess a detailed blueprint covering the eight essential pillars of compliance, from conducting a meticulous Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) to establishing a robust Data Breach Notification and Response protocol. This isn't just about avoiding fines; it's about building a sustainable framework for data governance that respects user privacy and fosters trust.
The journey, however, doesn't end with ticking off boxes. True, lasting compliance is dynamic, not static. It requires a fundamental shift from a reactive, audit-focused mindset to a proactive culture of "Privacy by Design." The principles we've explored, such as implementing clear processes for Data Subject Rights and maintaining detailed Records of Processing Activities (ROPA), are not one-time projects. They are living processes that must be integrated into the very fabric of your product development lifecycle, marketing campaigns, and daily operations.
Key Takeaways and Your Path Forward
As you transition from checklist to culture, keep these core takeaways at the forefront of your strategy. They represent the most critical shifts in thinking and practice required for long-term success.
- Proactive vs. Reactive: Don't wait for a data subject request or a potential breach to test your systems. Proactively embed privacy controls into new features from the initial design phase. Privacy by Design isn't a suggestion; it's a mandate for building user-centric, trustworthy products.
- Documentation is Your Defense: Your ROPA and DPIA documents are more than just paperwork. They are your primary evidence of due diligence and accountability. Treat them as essential strategic assets that require regular review and updates, especially when launching new products or entering new markets.
- Empowerment Through Rights: View Data Subject Rights not as a burden but as an opportunity. Providing seamless access, rectification, and erasure capabilities demonstrates respect for your users' autonomy. This transparency is a powerful differentiator that can significantly enhance brand loyalty.
Your immediate next step is to conduct a gap analysis. Use the eight points from this article as your benchmark. Where are you strong? Where are the vulnerabilities? Prioritize the most critical gaps, assign clear ownership to team members, and set realistic timelines for remediation. This isn't just a task for your legal team or a designated Data Protection Officer (DPO); it's a cross-functional responsibility. Engage your engineers, product managers, and marketers in this process to ensure everyone understands their role in upholding your organization's commitment to data privacy.
The True Value of Mastering GDPR
Mastering the concepts within this GDPR compliance checklist delivers value far beyond regulatory adherence. It positions your organization as a leader in an increasingly privacy-conscious world. When customers know you are a responsible steward of their personal information, they are more likely to engage with your services, trust your brand, and become long-term advocates. This trust is a tangible competitive advantage, translating directly into higher customer lifetime value and a stronger market position.
Ultimately, the goal is to make privacy an intuitive, integral part of how your organization operates. It should be a shared value that informs decisions from the C-suite to the front-line developer. By transforming this checklist into a living, breathing part of your company culture, you are not just complying with a regulation. You are future-proofing your business and building a foundation of trust that will pay dividends for years to come.
Ready to build GDPR compliance directly into your product experience? Formbricks offers open-source, in-product survey and feedback tools designed with privacy at their core, allowing you to gather crucial user insights without compromising on data protection. Start implementing a privacy-first feedback strategy today by exploring Formbricks and see how easy compliance can be.
Try Formbricks now


